Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMD157S)
| Drug Name |
Montelukast
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Brondilat; Montair; Singular; Apxi toxin; MK 0476; Brondilat (TN); MK-0476; Montelukast (INN); Montelukast [INN:BAN]; Singulair (TN); Sodium 1-(((1-(3-(2-(7-chloro-2-quinolinyl)ethenyl)phenyl)-3-(2-(1-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)phenyl)propyl)thio)methyl)cyclopropylacetate; {1-[({(1R)-1-{3-[(E)-2-(7-chloroquinolin-2-yl)ethenyl]phenyl}-3-[2-(1-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)phenyl]propyl}sulfanyl)methyl]cyclopropyl}acetic acid; (R-(E))-1-(((1-(3-(2-(7-Chloro-2-quinolinyl)ethenyl)phenyl)-3-(2-(1-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)phenyl)propyl)thio)methyl)cyclopropaneacetic acid; 1-((((1R)-1-(3-((1E)-2-(7-Chloro-2-quinolinyl)ethenyl)phenyl)-3-(2-(1-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)phenyl)propyl)thio)methyl)cyclopropaneacetic acid; 2-[1-[[(1R)-1-[3-[(E)-2-(7-chloroquinolin-2-yl)ethenyl]phenyl]-3-[2-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)phenyl]propyl]sulfanylmethyl]cyclopropyl]acetic acid
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiasthmatic Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
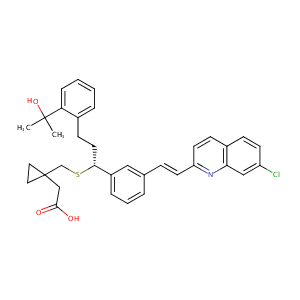 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 3 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 586.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 7.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Montelukast
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Montelukast (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Montelukast FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 3340). | ||||
| 3 | The COvid-19 Symptom MOntelukast Trial (COSMO) | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Critical Evaluation of Human Oral Bioavailability for Pharmaceutical Drugs by Using Various Cheminformatics Approaches | ||||
| 6 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 7 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 8 | Protective potential of montelukast against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Surg Res. 2010 Mar;159(1):588-94. | ||||
| 9 | As a potential treatment of COVID-19: Montelukast. Med Hypotheses. 2020 May 11;142:109828. | ||||
| 10 | Effects of polymorphisms of the SLCO2B1 transporter gene on the pharmacokinetics of montelukast in humans. J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Nov;53(11):1186-93. | ||||
| 11 | Effect of citrus juice and SLCO2B1 genotype on the pharmacokinetics of montelukast. J Clin Pharmacol. 2011 May;51(5):751-60. | ||||
| 12 | Substrates, inducers, inhibitors and structure-activity relationships of human Cytochrome P450 2C9 and implications in drug development. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(27):3480-675. | ||||
| 13 | In vitro metabolism of montelukast by cytochrome P450s and UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Drug Metab Dispos. 2015 Dec;43(12):1905-16. | ||||
| 14 | Determinants of cytochrome P450 2C8 substrate binding: structures of complexes with montelukast, troglitazone, felodipine, and 9-cis-retinoic acid. J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 20;283(25):17227-37. | ||||
| 15 | Karonen T, Filppula A, Laitila J, Niemi M, Neuvonen PJ, Backman JT "Gemfibrozil Markedly Increases the Plasma Concentrations of Montelukast: A Previously Unrecognized Role for CYP2C8 in the Metabolism of Montelukast." Clin Pharmacol Ther (2010):. [PMID: 20592724] | ||||
| 16 | Product Information. Singulair (montelukast). Merck & Co, Inc, West Point, PA. | ||||
| 17 | Product Information. Tukysa (tucatinib). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Piqray (alpelisib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 19 | Product Information. Korlym (mifepristone). Corcept Therapeutics Incorporated, Menlo Park, CA. | ||||
| 20 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Canadian Product Information.". | ||||
| 21 | Jerntorp P, Almer LO "Chlorpropamide-alcohol flushing in relation to macroangiopathy and peripheral neuropathy in non-insulin dependent diabetes." Acta Med Scand 656 (1981): 33-6. [PMID: 6953748] | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Copiktra (duvelisib). Verastem, Inc., Needham, MA. | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Fycompa (perampanel). Eisai Inc, Teaneck, NJ. | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
